Advancements in Automated Warehousing Technology
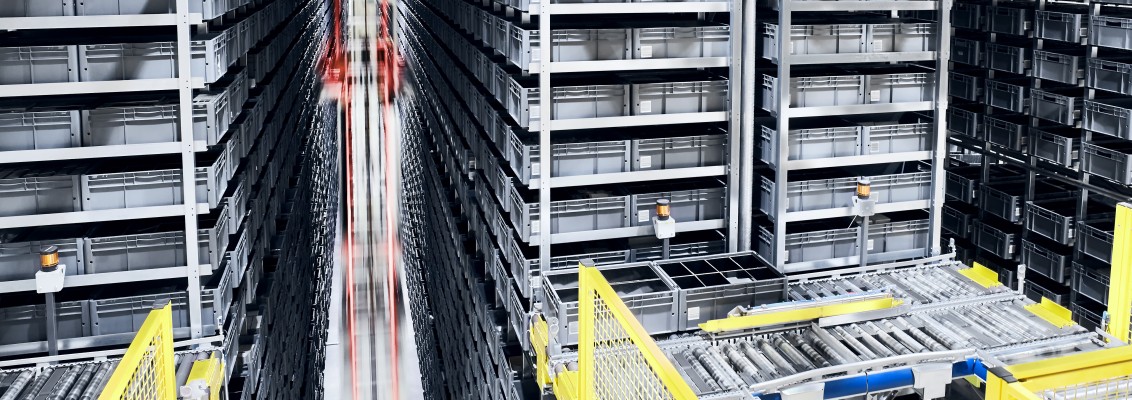

In today’s automated warehousing industry, Amazon and Walmart have distinctly established themselves as the household names of global consumers. How did they achieve such a demand of consumer usability and market share? They designed an infrastructure so that their customers at the push of a few buttons, could quickly purchase and receive almost anything they want or need without having to step outside their house, except maybe to grab the package they ordered just a few days earlier.
The brilliance of this application is its simplicity and ease of access to its users. What is not so simple is the actual infrastructure itself. Warehouse automation involves so many moving and programmable components that if any of those components are not functioning properly, it disrupts the entire flow of goods moving from point A to point B. From the automated storage and retrieval system and the conveyor system down to the pick-and-place center, getting inventory sorted, packaged, labeled and shipped properly is a very complex process. Even the cable and electrical system solutions being specified for these components, which can range from static power and data cables to pre-assembled, continuous-flex cables or torsion cables for drag chain or robotic applications, respectively, add another level of complexity to ensure the longevity of the system itself and the safety for its users. Designing a robust, efficient and competitive automated system is a delicate balance for everyone involved. Once the system is commissioned, the facility’s operation becomes almost completely self-sufficient with just ongoing routine maintenance and control station monitoring oversight.
Automated Warehouse Overview
The automated warehouse structure varies between industries, but they include some of the following areas and applications:
Control Station - key point for controlling and monitoring manufacturing and logistics processes.
Control Panel - stationary or mobile device with display and/or keyboard for operating machines and systems.
Pick & Place Area - device that independently grips, sorts and places goods or workpieces.
Conveyor System - stationary conveyor system for transporting various goods or workpieces.
6-Axis Robot - articulating robotic arm with six axes of movement for carrying out a wide range of movements and tasks.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) - mobile transporter with its own travel drive, which is automatically controlled and guided without contact.
Labeling Area - used to apply barcodes or labels to goods and workpieces.
Stacker Crane - rail-guided, single-track vehicle used to store and retrieve goods in a high-bay warehouse.
High-bay Warehouse - storage area with permanently installed shelving units where goods or workpieces are stored vertically.
Cable Trays - load-bearing structure made of sheet metal or plastic for routing and protecting cables and wires.
Moving Goods Internally
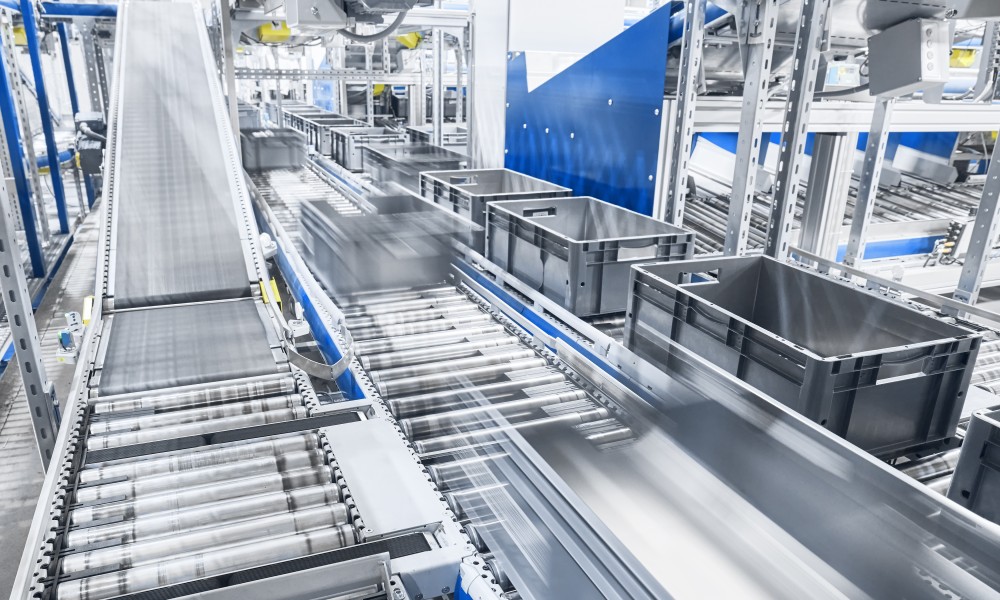

As conveyors and automation components require significant technical aptitude and focus from both designer and supplier, pairing artificial intelligence and robotics with your warehouse automation moves things to another level. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can interoperate algorithms, and independently move inventory to and from dedicated areas around the clock. Traditional multi-axis robots pick, sort and place products as well as handle heavier products that employees can’t manage without assistance. This improves not only efficiencies but safety as well.
Amazon has over 520,000 robots working in unison with their automated warehouses and have added over one million jobs worldwide to transform their business. Walmart and partner Symbotic are deploying and retrofitting all 42 of Walmart’s regional distribution centers over the next 10 years with robots. These industry leaders are paving the way in industrial automation, which is starting to see smaller companies with sizable warehouses follow suit as it relates to warehouse automation and efficiencies just to stay competitive. The importance of factory floor space, fulfillment process flow, reducing idle and/or downtime, and improving employee safety and efficiencies is critical to these types of business models.
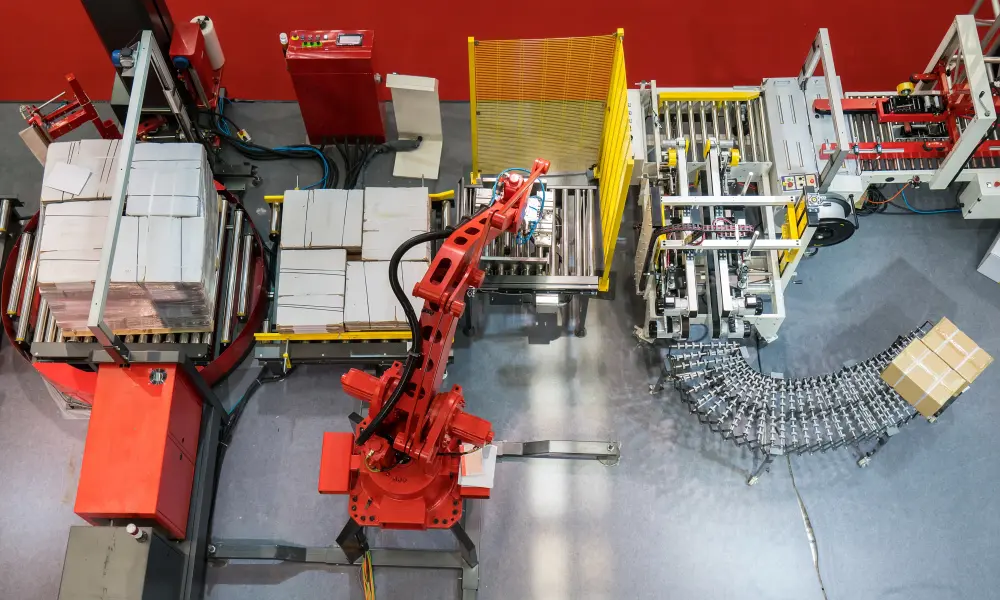
With these factors in play and more within the infrastructure of an automated facility, you also have to be fully prepared to respond to any electrical, mechanical or software issues that can create significant delays to consumers or end users and revenue loss. Robust and sustainable cable systems are key to the life of the automated warehouse, so qualifying and selecting the right component manufacturer and/or electrical system supplier becomes more important than ever. Suppliers who control not only the design quality and manufacturing of their products but also provide the added value of complete component and electrical system solutions for automated applications quickly rise to the top.
Why Partner with HELUKABEL
HELUKABEL has been providing electrical connection technology solutions for the automated warehousing space since 2001. We specialize in the production of cables, wires, accessories, cable assemblies, and guidance and protection systems found in today’s cutting-edge automated warehouse equipment. HELUKABEL offers a wide array of flexible and continuous-flex control, data, network and bus, VFD/servo power and feedback cables to reliably transmit power and data to keep materials on the move in storage facilities throughout the world.
With subsidiaries EKD Systems providing premium drag chains in plastic and steel, Sangel Systemtechnik offering plug-and-play cable assemblies and industrial luminaries, and Kablemat Wicheltechnik specializing in cable management with advanced winding and measuring machines, HELUKABEL’s ability to provide solutions from bulk cable to complete, plug-and-play cable sub-assemblies makes us the one-stop shop for complete electrical system solutions within the automated warehouse ecosystem.
Automated Warehouse Ecosystem
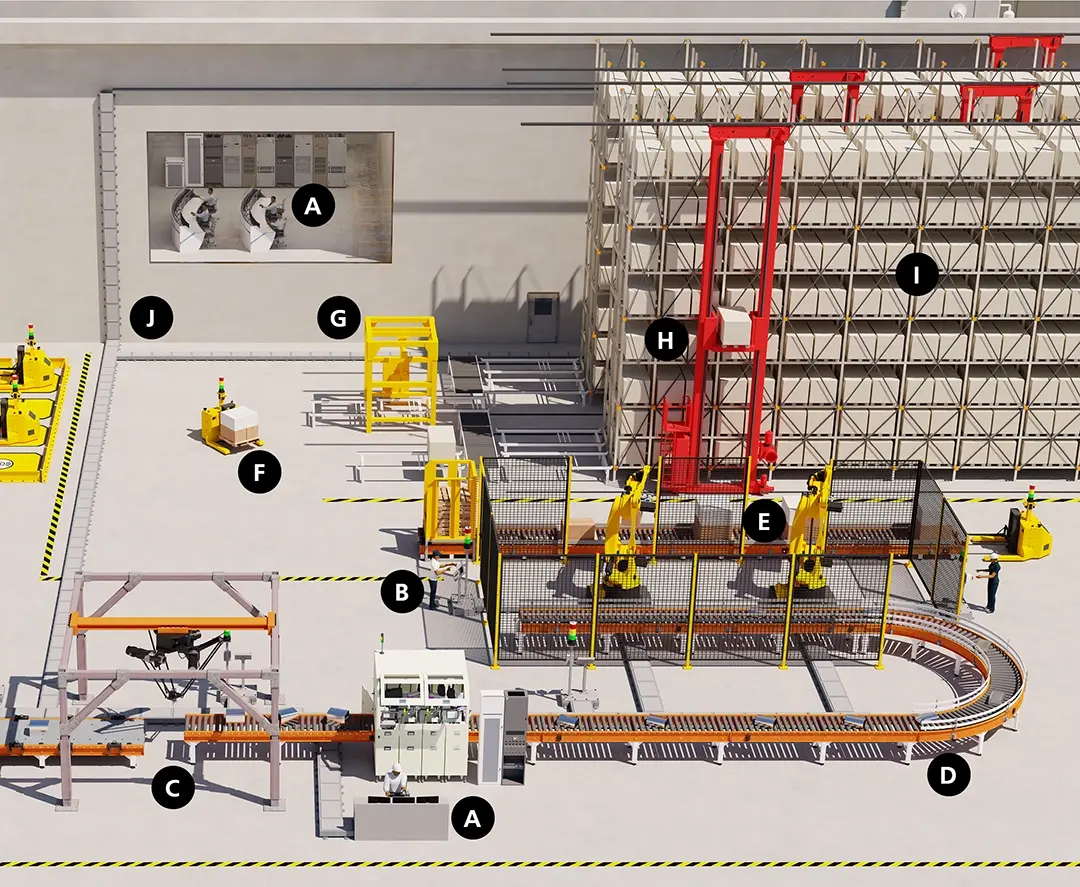
Electrical System Solutions for Automated Warehousing
A - Control Station
[1] [5] [6] [8] [9] [12]
B - Control Panel
[1] [3] [6] [8] [9] [11] [12]
C - Pick & Place Area
[1] [2] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] [13] [14]
D - Conveyor System
[1] [2] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12]
E - 6-Axis Robot
[1] [2] [3] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [15]
F - Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV)
[1] [2] [5] [6] [8]
G - Labeling Area
[1] [4] [5] [6] [8] [9] [12] [13] [14]
H - Stacker Crane
[1] [2] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [12] [13]
I - High-bay Warehouse
[1] [2] [4] [5] [7] [8] [9] [12] [13]
J - Cable Trays
[1] [2] [5] [11] [12]
[1] Data Cables (Bus/Ethernet/Fiber Cables)
HELUKAT® & HELUCOM®
[2] Drive Cables (Servo/Feedback/Hybrid)
TOPFLEX®, TOPSERV® & TOPGEBER®
[3] Robotic Cables
ROBOFLEX®
[4] Drag Chain Cables
HELUCHAIN®, MULTIFLEX 600, MULTIFLEX 512®, MULTISPEED®,
Single 602-RC , SUPERTRONIC®, SUPER-PAAR-TRONIC-C-PUR®
[5] Machine & Facility Infrastructure Cables
HELUPOWER®, HELUCONTROL®, HELUDATA®, MEGAFLEX®, TRAYCONTROL®, FIVENORM, HELUTHERM® & Single 600
[6] Pre-assembled Cables (Data/Drive Technology)
RJ45, M12 & M8 Patch Cables, OEM Servo, Motor & Feedback
[7] HELUKAT® Data Connectors
[8] HELUTEC® Circular Connectors
[9] HELUTOP® Cable Glands
[10] Grounding Components
EMC glands, copper grounding straps
[11] Conduit & Protective Tubing
HELUcond
[12] Tools & Accessories
[13] EKD Systems Drag Chains
[14] SANGEL® Systemtechnik - Industrial Luminaires
[15] Robotic Dress Packs
The product families listed above are a consolidated overview and not our comprehensive portfolio of available solutions. For more information on our electrical system solutions for automated warehousing, please contact us.
ARTICLE DOWNLOAD
Click here to view this article in our digital download centre.
